File:400ft-intrusion.png
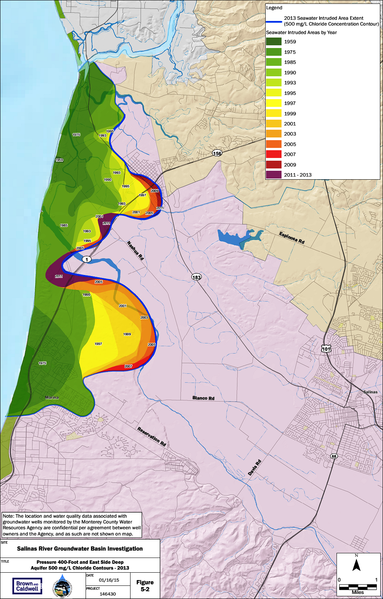
Summarizes the rates of seawater instrusion from 1944 to 2013 for the 400-foot aquifer in the Salinas Valley, as measured from the historical extents. Chloride concentration is used as an indicator of seawater intruded into aquifers because chloride behaves conservatively (i.e. non-reactively) in aquifer materials; hence, chloride moves at approximately the same rate as groundwater. The 500 milligrams per liter (mg/L) chloride (Cl) level is the target concentration that Monterey County Water Resources Agency (MCWRA) uses to demarcate the landward edge of the seawater intrusion front. MCWRA samples dedicated monitoring and agricultural production wells each summer for chloride and the other major cations and anions to document groundwater quality. Chloride concentration is used as the primary proxy for the evaluation of seawater intrusion, along with other geochemical tools. The acres advanced rates were estimated by MCWRA.
Image from State of the Salinas River Groundwater Basin Report (Jan. 2015) http://www.mcwra.co.monterey.ca.us/hydrogeologic_reports/documents/State_of_the_SRGBasin_Jan16_2015.pdf
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 15:35, 29 March 2016 |  | 989 × 1,547 (1.18 MB) | Gabem (Talk | contribs) | Summarizes the rates of seawater instrusion from 1944 to 2013 for the 400-foot aquifer in the Salinas Valley, as measured from the historical extents. Chloride concentration is used as an indicator of seawater intruded into aquifers because chloride b... |
- You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
There are no pages that link to this file.