United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE)
A organizational summary by the ENVS 560/L Watershed Systems class at CSUMB.
Contents
Overview
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) is an engineer formation of the U.S. Army that has three primary mission areas: engineer regiment, military construction, and civil works. USACE is the leading federal agency pursuing civil works projects ranging from flood control to ecosystem restoration, and has a significant reach and impact on the nation's natural resources and aquatic ecosystems. It oversees thousands of civil works projects and the Clean Water Act 404 Regulatory Program [1]. USACE has 37,000 civilian and military personnel, making it one of the world's largest public engineering, design, and construction management agencies.
History in California
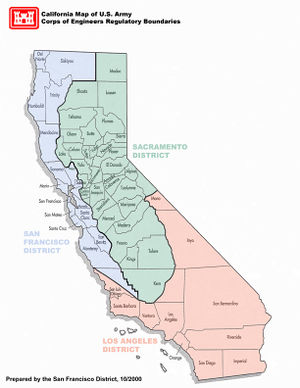
Divisions and Districts
USACE is organized geographically into eight permanent divisions, one provisional division, and one research command which reports directly to headquarters in Washington DC. Within each division there are several districts. Districts are defined by watershed boundaries for civil works projects and by political boundaries for military projects.
California is part of the South Pacific Division (SPD) which also covers Arizona, Nevada, Utah, and New Mexico, as well as portions of Oregon, Idaho, Wyoming, Colorado, and Texas [3].
The South Pacific Division includes the following four districts:
- Albuquerque
- Los Angeles
- Sacramento
- San Francisco
Central Coast
The San Francisco District oversees the California Central Coast Region.
Current Land Management
Division Commander
The Division Commander is directly responsible to the Chief of Engineers. The South Pacific District Commander directs and supervises the individual District Commanders. SPD Commander duties include:
- Preparing engineering studies and design
- Constructing, operating, and maintaining flood control, river, and harbor facilities and installations
- Administering the laws on civil works activities
- Acquiring, managing, and disposing of real estate
- Mobilization support of military, natural disaster, and national emergency operations [4]
Civil Works
Army civil works consists of three congressionally authorized business lines: navigation, flood and storm damage protection, and aquatic ecosystem restoration. Civil works is also tasked with administering the Clean Water Act Section 404 program, recreation, hydropower, environmental infrastructure, and water supply at the USACE flood control reservoirs. The civil works staff oversees construction, operation, and maintenance of dams, canals, and flood protection in the United States as well as a wide range of public works throughout the world [5].
The Conservation Fund
The Conservation Fund works with the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers in various ways. The Fund's Conservation Leadership Network partners with the Corps to provide annual training on mitigation banking, conservation baking, and in-lieu fee programs [6]. Mitigation banking is the preservation, enhancement, restoration, or creation of a wetland, stream, or habitat conservation area which offsets, or compensates for, expected adverse impacts to similar nearby ecosystems [7]. Conservation banking is an environmental market-based method designed to offset adverse effects to species that are of concern, threatened, or threatened and protected under the United States Endangered Species Act through the creation of conservation banks [8]. In-lieu fee programs involve the restoration, establishment, enhancement, and/or preservation of aquatic resources through funds paid to a government or non-profit natural resources management entity to satisfy compensatory mitigation requirements for Department of Army permits [9].
Other Activities
Hydrologic Engineering Center
The USACE Hydrologic Engineering Center (CEIWR-HEC) was formed in 1964 to institutionalize the technical expertise that became known as hydrologic engineering. Over the years, CEIWR-HEC developed and published a number of technical methods documents addressing the full range of hydrologic engineering and planning analysis technologies. CEIWR-HEC is organized into an Executive Office and three divisions: Hydrology and Hydraulics Technology; Water Resource Systems; and Water Management Systems. Notable recent achievements include: development of the next generation of successor CEIWR-HEC software (HEC-RAS, HEC-HMS, HEC-FDA, and HEC-ResSim); providing leadership in establishing risk analysis as the foundation technology for flood damage reduction planning and analysis; and development and deployment of the Corps Water Management System (CWMS), the real-time forecasting and decision-support system that is used 24/7 in execution of the USACE Civil Works water resource water control management mission [10]. CEIWR-HEC technologies are used around the world for hydrologic development and analysis.
References
- ↑ U.S. Department of Defense. The Conservation Fund. [Cited March 2021]
- ↑ U.S. Department of Defense. Regulatory Boundaries in California. [Cited March 2021]
- ↑ U.S. Department of Defense. Locations. [Cited March 2021]
- ↑ South Pacific Division. [Cited March 2021]
- ↑ United States Army Corps of Engineers. [Cited March 2021]
- ↑ U.S. Department of Defense. The Conservation Fund. [Cited March 2021]
- ↑ Mitigation Banking. [Cited March 2021]
- ↑ Conservation Banking. [Cited March 2021]
- ↑ In-Lieu Fee Programs. US Army Corps of Engineers. [Cited March 2021]
- ↑ U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Hydrologic Engineering Center. [Cited March 2021]
Disclaimer
This page may contain student work completed as part of assigned coursework. It may not be accurate. It does not necessary reflect the opinion or policy of CSUMB, its staff, or students.