The California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA)
This page provides a general overview of California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA). This act requires any development with potential impact to the environment to go through a detailed review process.
History
In response to the January 1, 1970 passage of the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), the California Assembly created the Assembly Select Committee on Environmental Quality to study the possibility of supplementing NEPA on a state level. In 1970, the committee issued a report entitled The Environmental Bill of Rights that called for a California counterpart to NEPA. Acting on that recommendation, the State Assembly passed CEQA in 1970. [1] The original Act was very short, taking only three pages in the Statutes of California, and did not define any terms. Interpretation of the Act fell to the courts in cases such as Environmental Defense Fund vs. Coastside County Water District and Friends of Mammoth vs. Board of Supervisors. CEQA took on its modern form with the passage of a legislative amendment in 1976 that made the standards of the Act much more explicit. [2]
Process
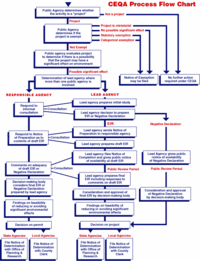
The procedures of CEQA are outlined here:
- An activity is examined to determine if it fits the characteristics of a CEQA project.
- If the activity is found to be a project, it is checked to see if any exemptions apply to it.
- If an exemption may apply, a Notice of Exemption (NOE) is filed.
- If not, an initial study is performed.
- An initial study generally follows the CEQA Guidelines. These guidelines include a checklist which investigate the project's impact to: Aesthetics,Agricultural Resources, Air Quality, Biological Resources, Cultural Resources, Geology and Soils, Hazards and Hazardous Materials, Hydrology and Water Quality (Hydrology and Water Quality Components of Central Coast CEQA Documents), Land Use and Planning, Mineral Resources, Noise, Population and Housing, Public Services, Recreation, Transportation/Traffic, Utilities and Service Systems, and Mandatory Findings of Significance.
- The Lead Agency determines whether there are possible impacts to the environment from the project. If so, an Environmental Impact Report (EIR) is performed. If not, the outcome is a Negative Declaration (ND). Both an EIR and ND are posted for public review through State Clearinghouse which is part of the Governor's Office of Planning and Research where CEQAnetfunctions as an online database. Both documents are subject to review and comments from agencies, organizations, and the general public.
- Following the review period, the Lead Agency takes all comments into consideration and may update the document. After completion and determining to continuing the project, the Lead Agency files a notice of determination (NOD).[3]
Agencies
There are three particular types associated with CEQA:
- Lead Agency
- Agency primarily accountable for project approval. Non-profits cannot be Lead Agencies.
- A detailed list of Agencies that are lead applicants in CEQA
- Responsible Agency
- Agency legally charged with project approval.
- Trustee Agency
- Agency that has jurisdiction over a resource in trust for the people of California. Does not have legal responsibility over project.
Court Cases
Since its passage the courts have played an important role in interpreting CEQA. Some important cases have included:
- Environmental Defense Fund vs. Coastside County Water District (1972)
- Friends of Mammoth vs. Board of Supervisors (1972)
- No Oil Inc. vs City of Los Angeles (1974)
- Citizens to Preserve Ojai vs. County of Ventura (1985)
- Resource Defense Fund vs. Local Formation Agency (1987)
- Citizens for Quality Growth vs. City of Mount Shasta (1988)
- Laurel Heights Improvement Association vs. Regents of the University of California (1988)
A complete list of court cases affecting CEQA is maintained by the California Natural Resources Agency and CERES. Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
- Several additional document types exist.
- Useful term definitions
References
- ↑ CEQA- Frequently Asked Questions [1]
- ↑ A Primer on CEQA [2]
- ↑ CEQA Understanding the Basics SWRCB[3]
Links
- ENVS 560/L Watershed Systems
- CEQA projects on Central Coast
- CEQA review and land use planning
- California Coastal Commission
- Agencies that are lead applicants in CEQA
- Hydrology and Water Quality Components of Central Coast CEQA Documents
- List of Environmental Consultants in the Central Coast Area
Disclaimer
This page may contain students's work completed as part of assigned coursework. It may not be accurate. It does not necessarily reflect the opinion or policy of CSUMB, its staff, or students.